Bio Gas
- Home
- Bio Gas
Type Of Services
- Bio Gas
- Demineralization Plant
- Commercial RO Plant
- Industrial RO Plant
- RO Desalination Solutions
- Effluent Treatment Plant (ETP)
- Membrane Bio Reactor (MBR)
- Membrane Aerated Biofilm Reactor (MABR)
- Moving Bed Bio Reactor (MBBR)
- Organic waste composter (OWC)
- Commercial RO Plant
- Sequence Batch Reactor (SBR)
- Sewage Treatment Plant (STP)
- Softener Plant
- Ultra Filtration
- Zero Liquid Discharge Treatment (ZLD)
- Solar Plant
Bio Gas
Bio Gas is most commonly also known as Biomethane. It’s also sometimes called marsh gas, sewer gas, compost gas and swamp gas in the US.
Bio Gas is a naturally occurring and renewable source of energy, resulting From the breakdown of organic matter. Biogas is not to be confused with ‘Natural’ gas, which is a non-renewable source of power.
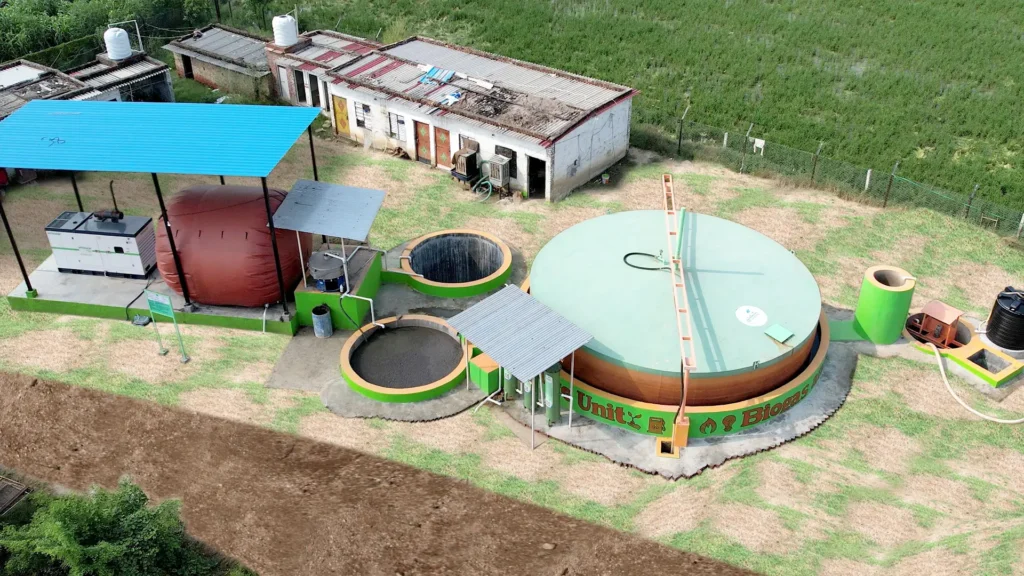

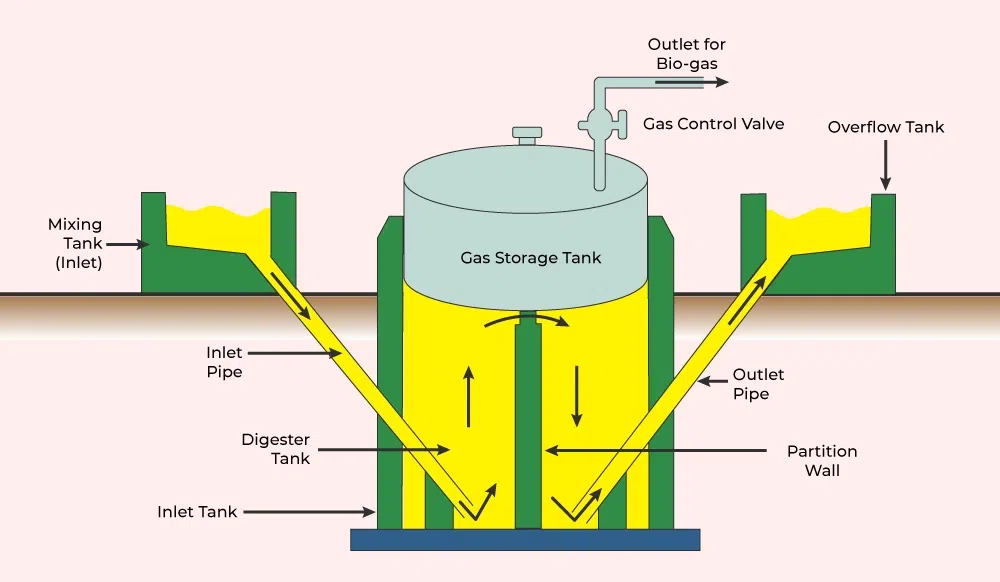
How Does Biogas Work?
- Feedstock Collection – Organic waste like food scraps, manure, and crop residues is collected.
- Anaerobic Digestion – Microorganisms break down the waste in an oxygen-free environment, producing biogas.
- Gas Collection – The produced methane-rich biogas is collected in a storage system.
- Utilization – Biogas is used for cooking, electricity generation, heating, or as vehicle fuel.
- Byproduct (Digestate) Usage – The leftover material, known as digestate, is used as a nutrient-rich organic fertilizer.
Advantages of Biogas
- Reduces dependence on fossil fuels.
- Converts waste into energy, reducing landfill waste.
- Lowers greenhouse gas emissions, helping combat climate change.
- Produces organic fertilizer as a byproduct, improving soil health.
- Cost-effective and sustainable energy source.
- Reduces indoor air pollution compared to traditional wood or charcoal cooking.
- Provides energy security in rural and off-grid areas.
Applications of Biogas

Cooking Fuel
Electricity Generation

Vehicle Fuel (Bio-CNG)

Industrial Use

Waste Management


